01/07/2025 8:47 p.m.
http://cablematic.iskra.cat/en/products/axpert-ks-pure-wave-inverter-for-pv-pv-4-kva-SA135/
http://cablematic.iskra.cat/en/products/axpert-ks-pure-wave-inverter-for-pv-pv-4-kva-SA135/
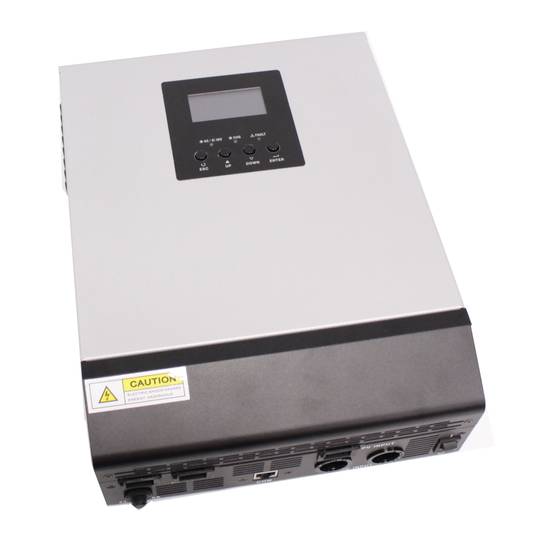
Axpert KS pure wave inverter for PV PV 4 KVA
REF: SA135
RENEWED
It comes from return with some slight mark of invaluable use.
Original product specifications
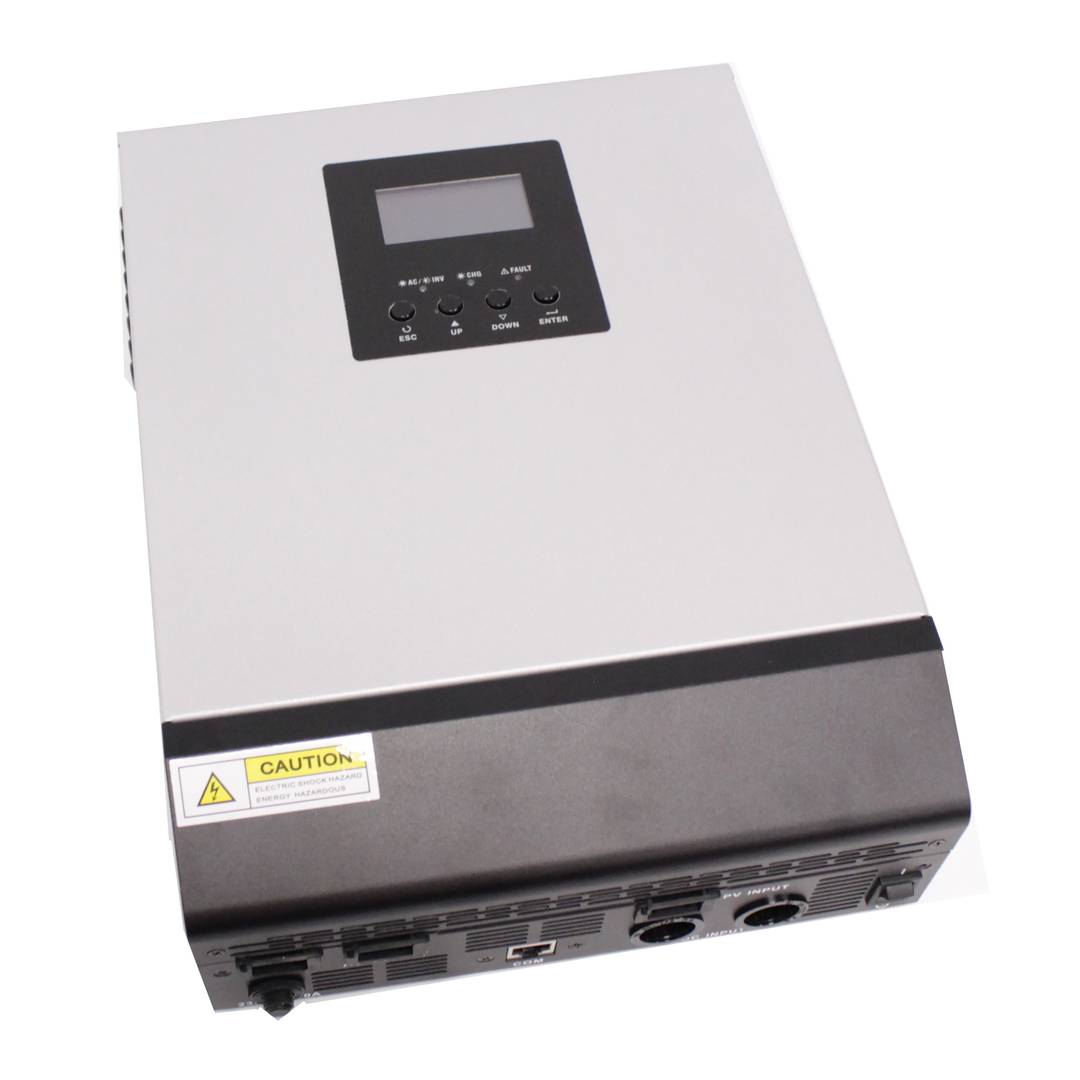
- Pure sine wave inverter. Model with capacity of 4000 VA, recommended for a load of up to 3200 W.
- Input voltage range configurable through the LCD panel.
- Configuration of the battery charge configurable through the LCD panel.
- Possibility of configuring different modes of orbased on the priority and availability of solar energy, VAC and battery charge.
- The VAC input is connected to the public electricity grid or to its own power generation system.
PVP
€147.08
You save 58.83
Price including VAT:
€147.08
PVD
€122.76
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
warranty
RENEWED
safe
Original product specifications
- Pure sine wave inverter. Model with capacity of 4000 VA, recommended for a load of up to 3200 W.
- Input voltage range configurable through the LCD panel.
- Configuration of the battery charge configurable through the LCD panel.
- Possibility of configuring different modes of orbased on the priority and availability of solar energy, VAC and battery charge.
- The VAC input is connected to the public electricity grid or to its own power generation system.
Original product info
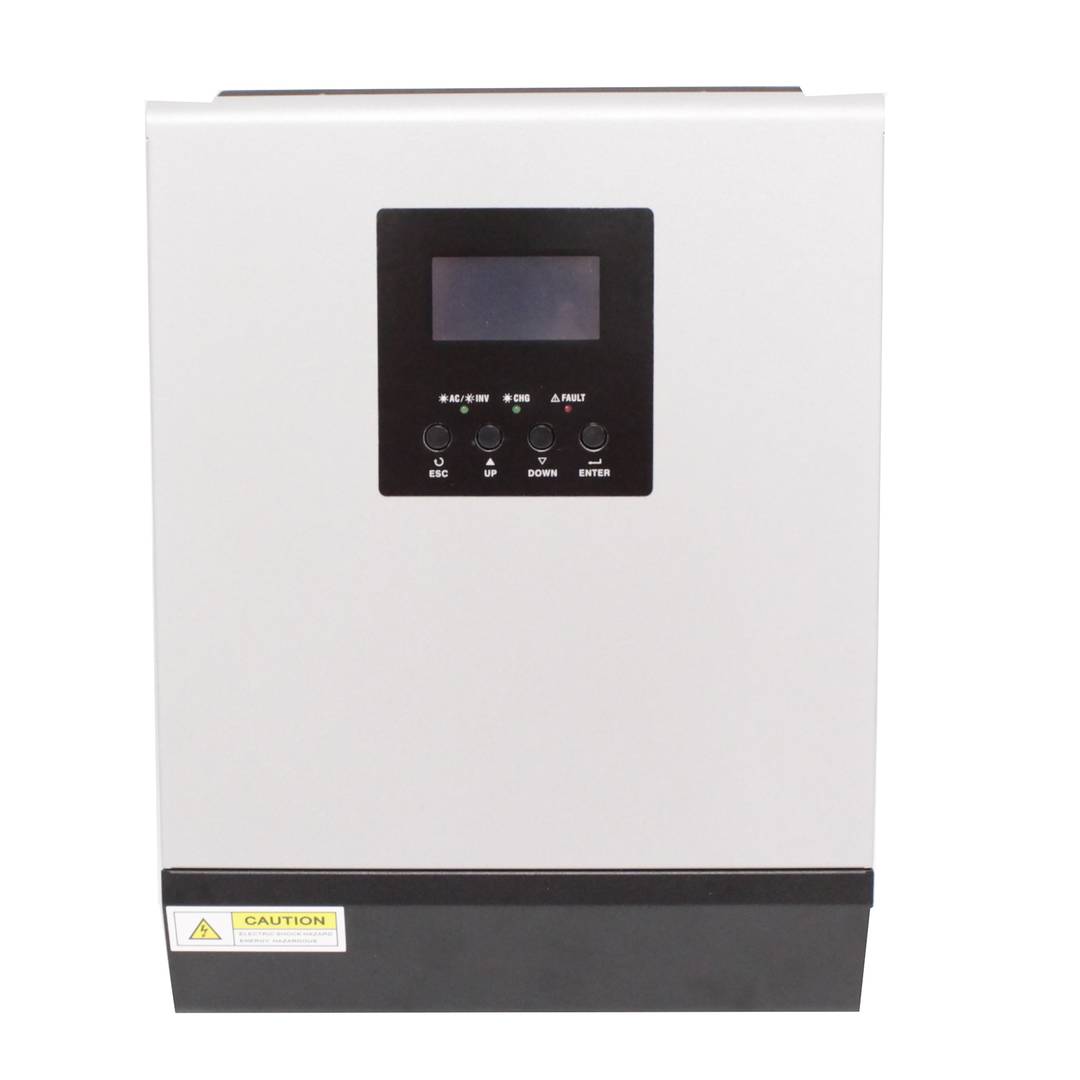
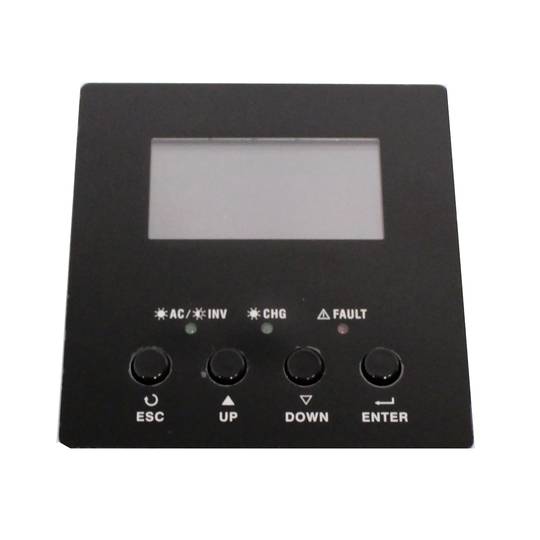
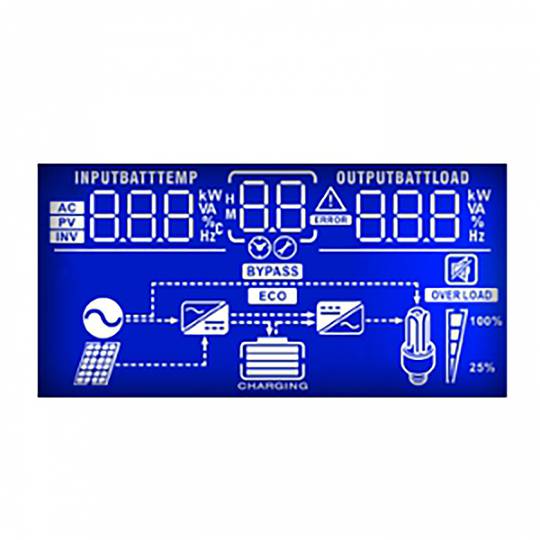
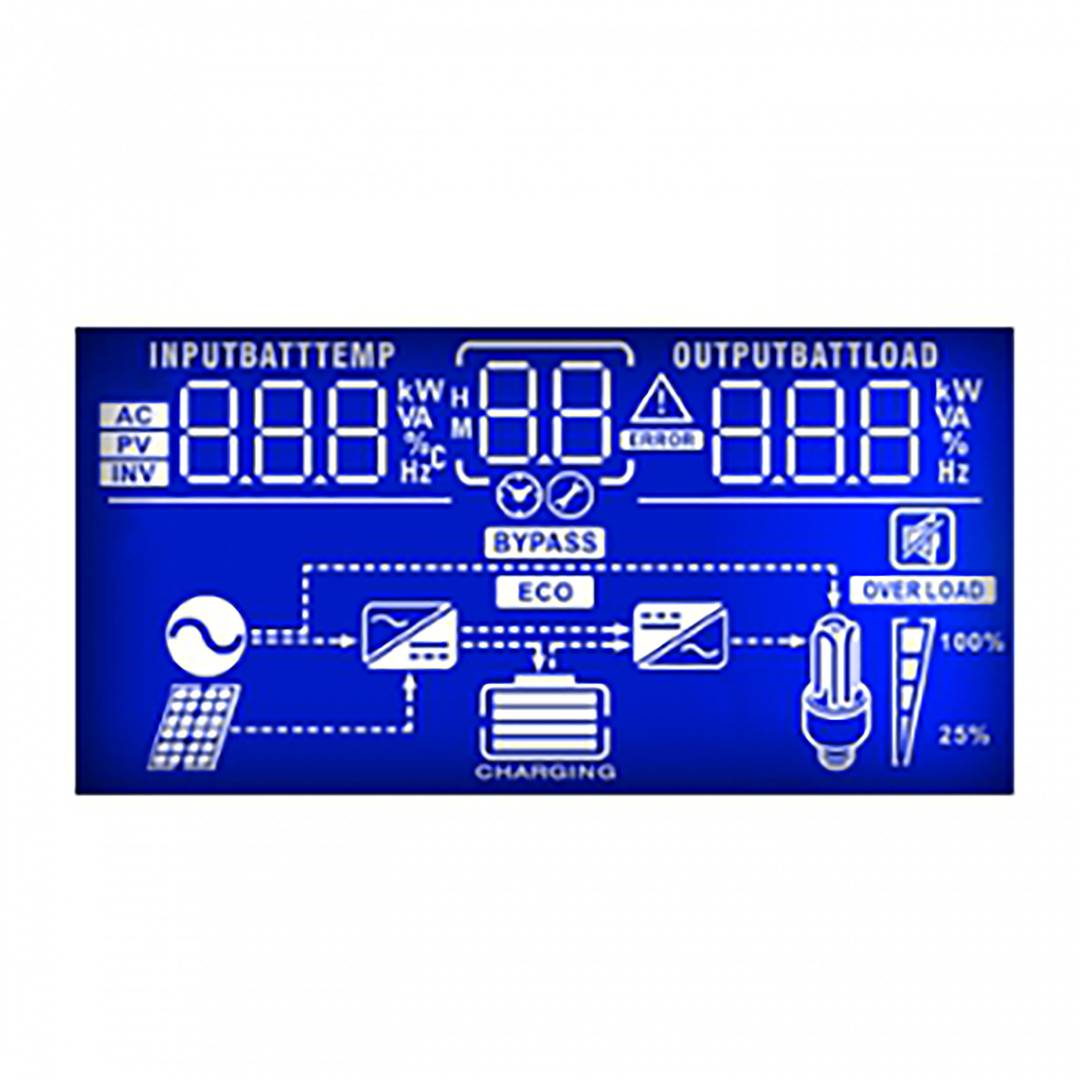
Inverter and charger of the Axpert range. Device oriented to be used in photovoltaic (PV) solar energy applications and with multiple functions: pure wave inverter, solar charger and battery charger to offer uninterrupted power supply. Its large LCD screen allows the user to program, as well as easy access to functions thanks to the push buttons on the front panel. It offers functions such as charginge batteries, set the priority of the solar charger, etc.
Specifications
Specifications
- Pure sine wave inverter. Model with capacity of 4000 VA, recommended for a load of up to 3200 W.
- Input voltage range configurable through the LCD panel.
- Configuration of the battery charge configurable through the LCD panel.
- Possibility of configuring different modes of orbased on the priority and availability of solar energy, VAC and battery charge.
- The VAC input is connected to the public electricity grid or to its own power generation system.
- Automatic restart while the VAC current is recovering.
- Protection against overload, temperature and short circuits.
- Efficient design to optimize the battery charge.
- Functionof cold start.
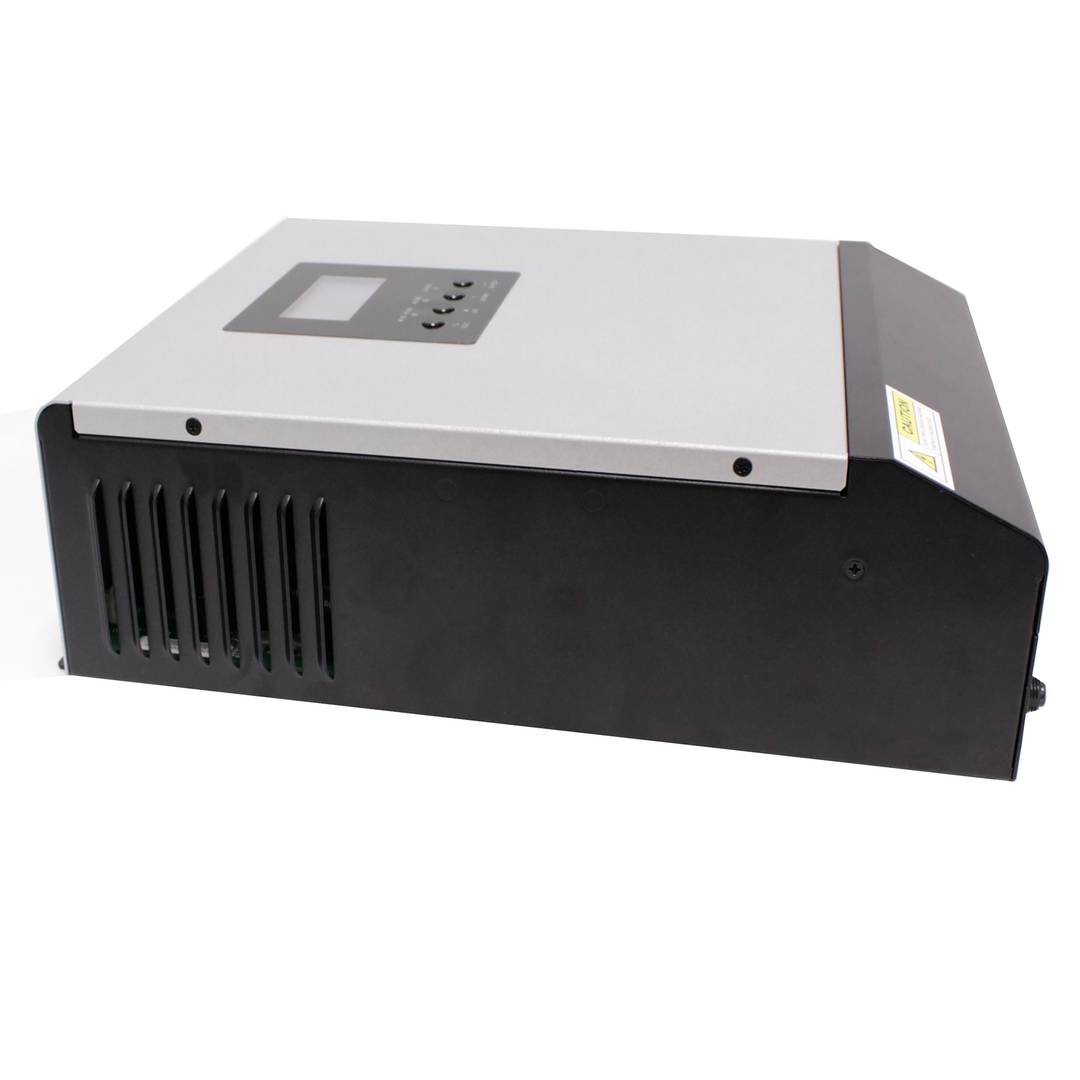
- Compact design, mounted on metal chassis recessed in wall.
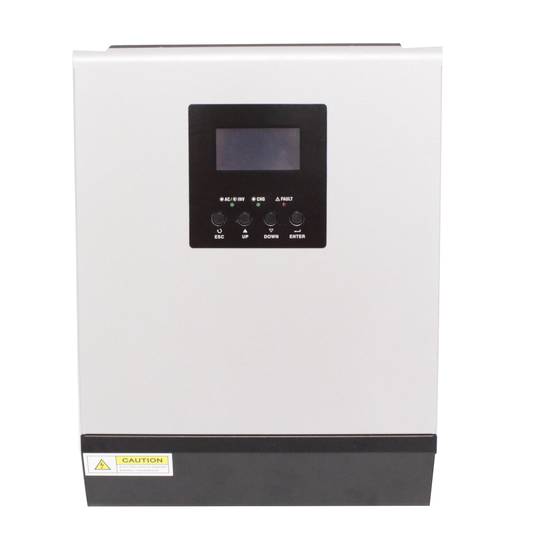
- LCD display, 3 status LEDs and 4 buttons for programming.
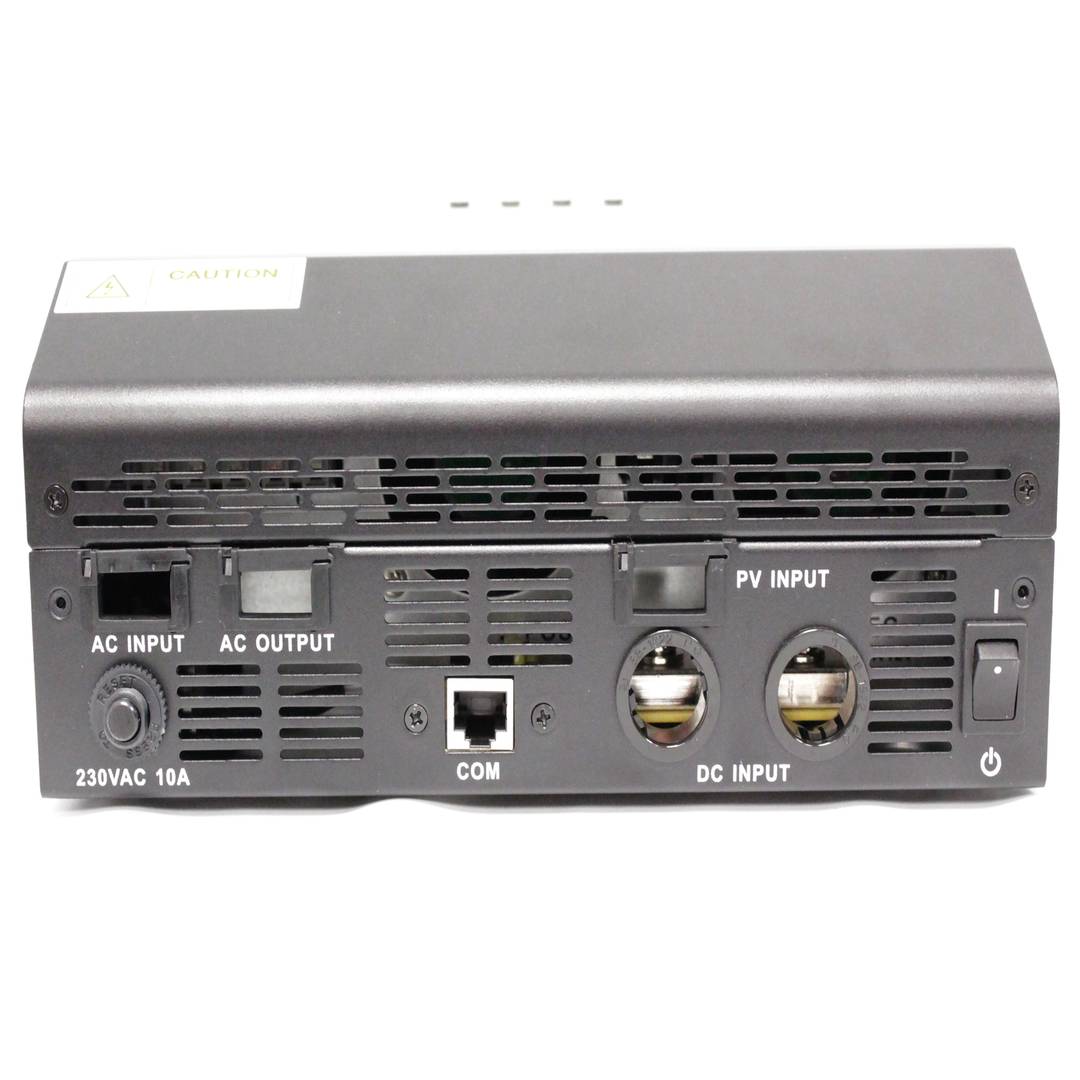
- ON/OFF switch and 230VAC/10A circuit breaker protector.
- Size (depth x width x height): 115 x 295 x 455 mm.
- Weight: 9.8 Kg.
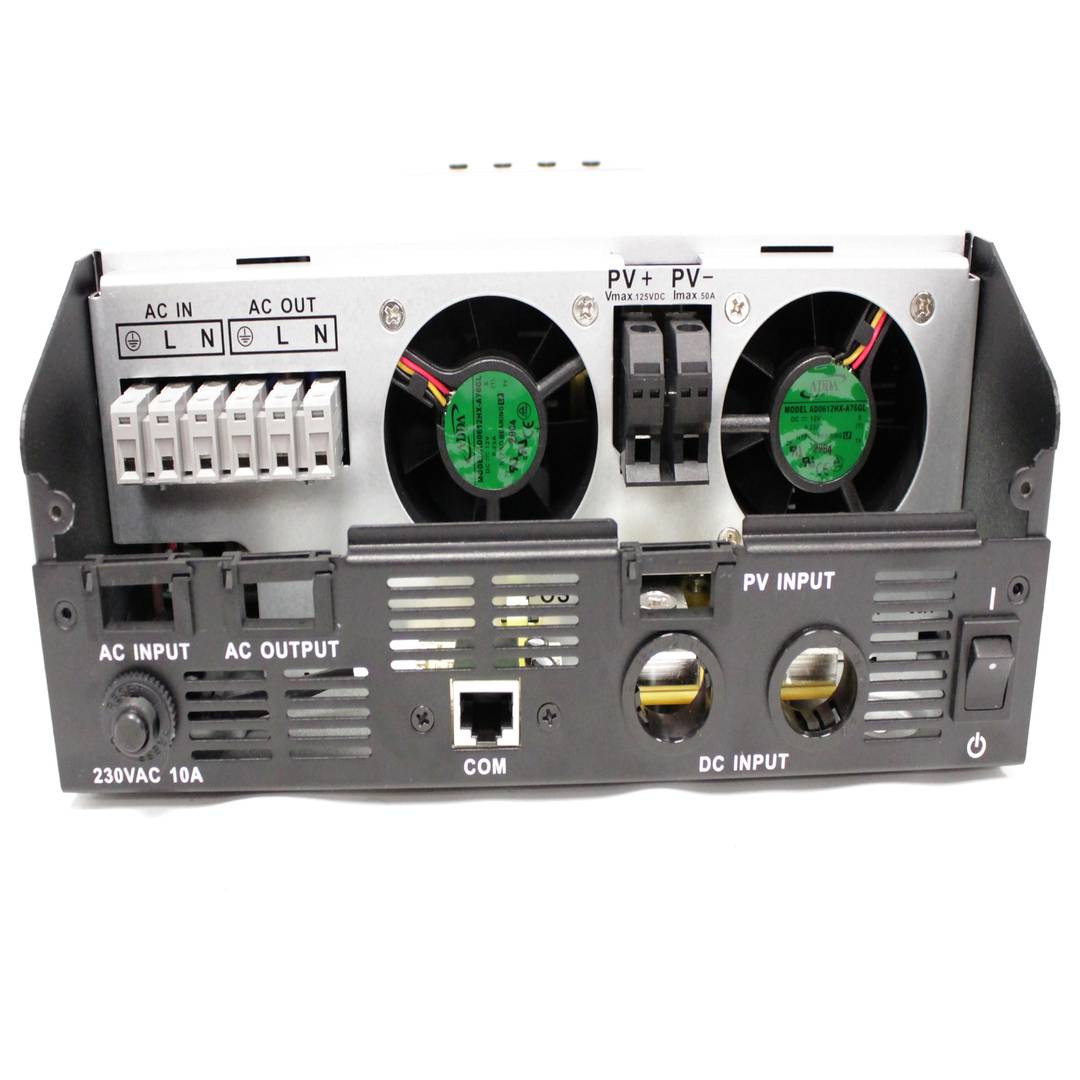
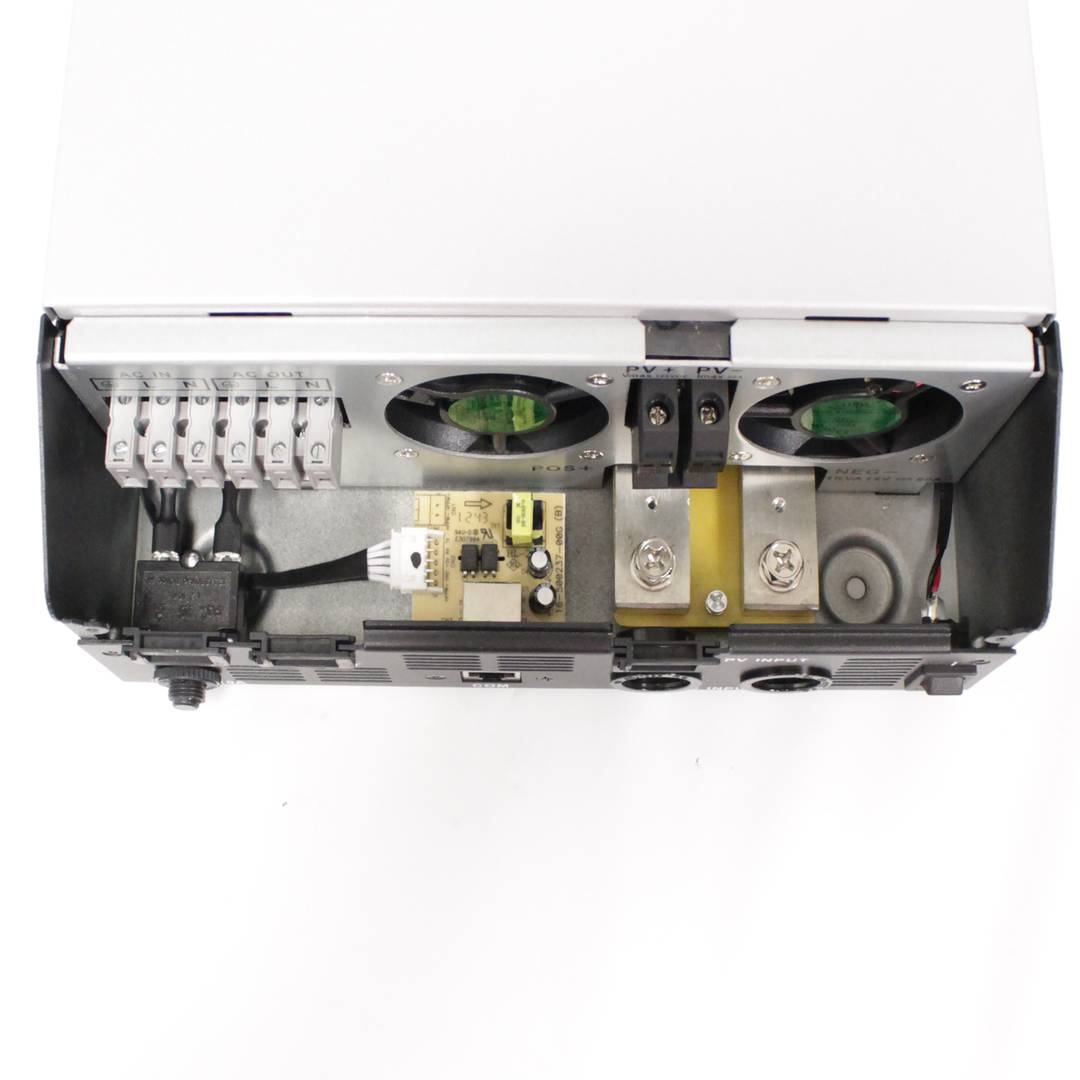
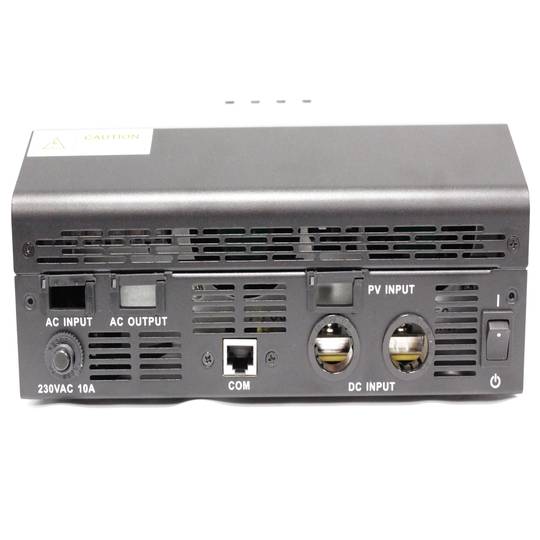
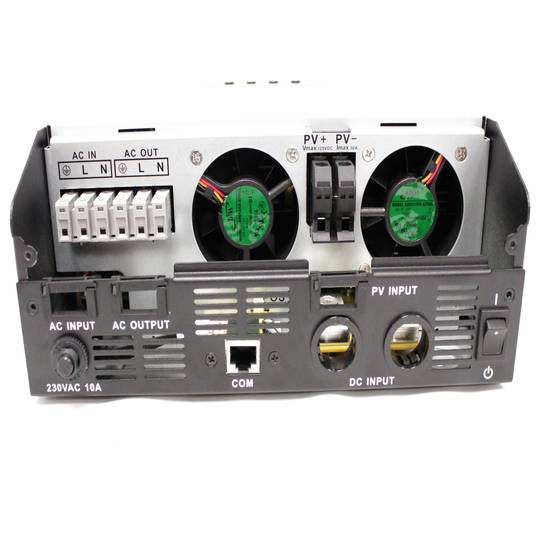
- VAC power input from the power gridAC or other AC generation systems (L, N and G).
- Current output VAC (L, N and G) that is connected to the domestic electrical circuit.
- Input of photovoltaic energy (PV + and PV-).
- Connection of battery system (POS + and NEG-).
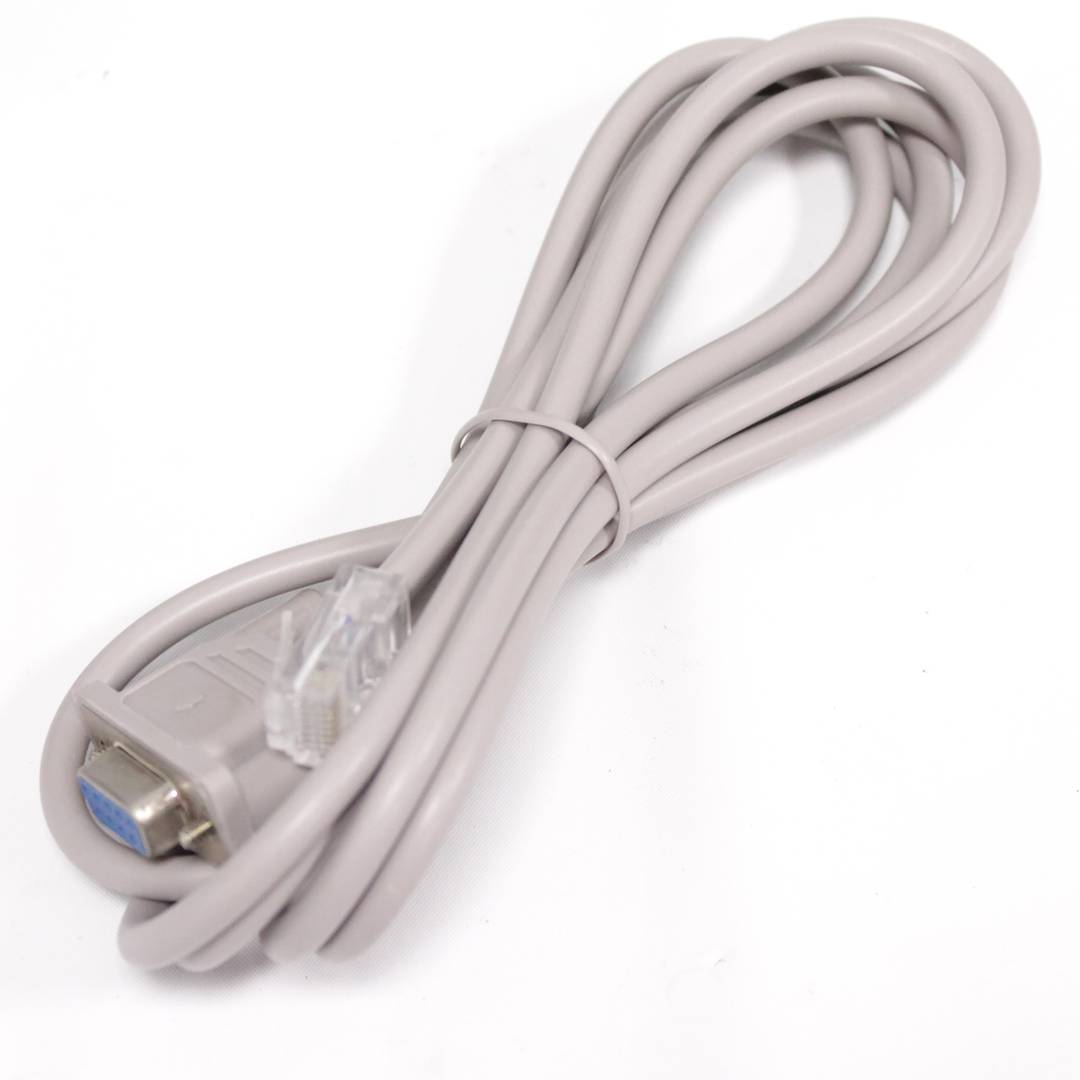
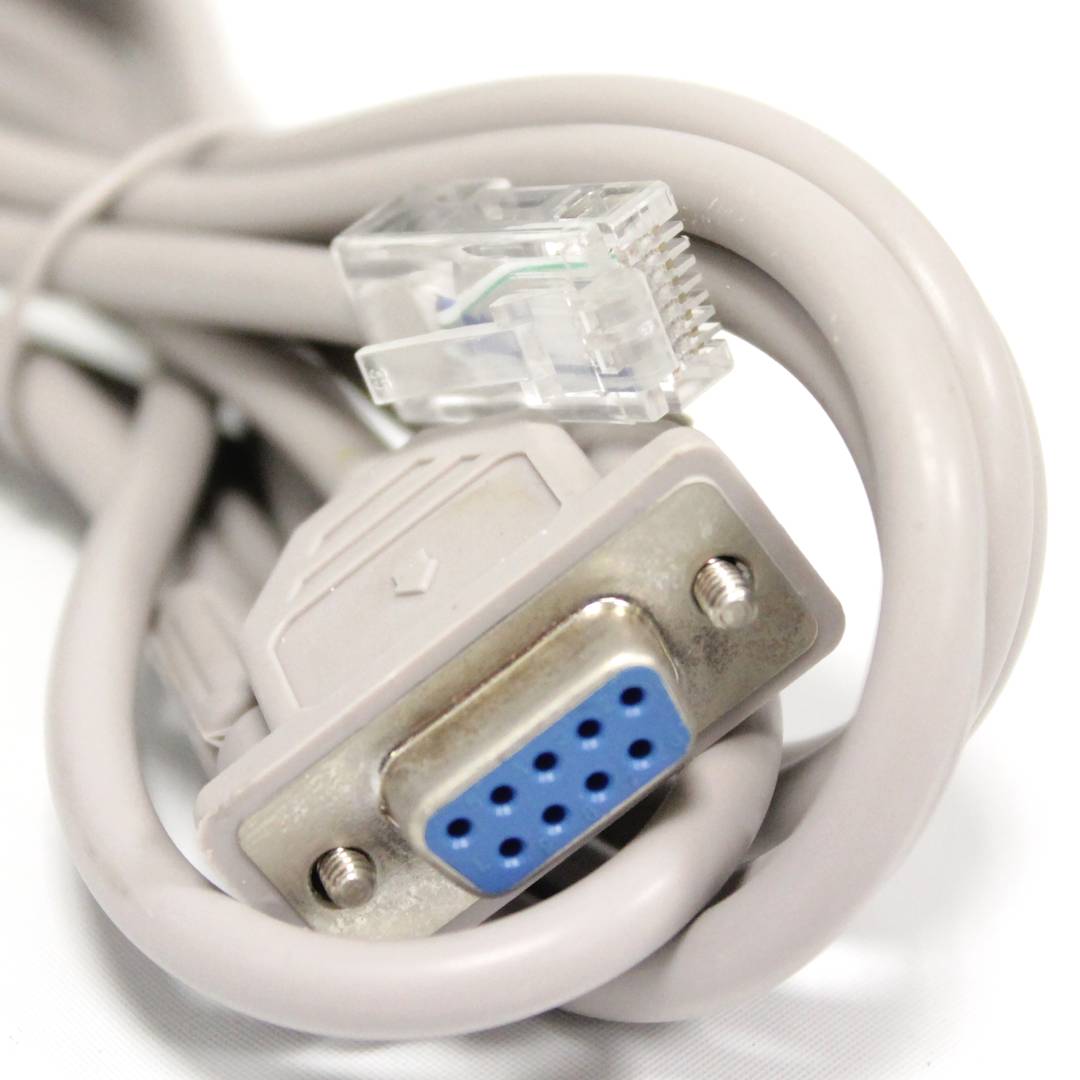
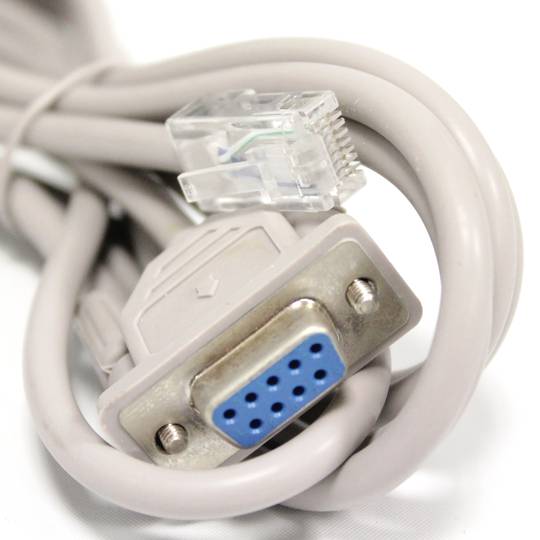
- RJ45 communications port female. RS232 serial cable (RJ45 male to DB9 female) is supplied.
- Gross Weight: 11.0 kg
- Number of packages: 1
- Master-pack: 1
Technical terms
- Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaic energy is produced by solar radiation using devices called photovoltaic cells. It is ideal for supplying all kinds of isolated houses, shelters, but also can be used to supply electricity on a large scale. We show the operating principle "In a semiconductor exposed to light, a photon of energy starts an electron, creating both a" gap "in the atom excitador. Normally, the electron quickly finds another hole to refill it, and the energy provided by the photon thus dissipates as heat. The principle of a photovoltaic cell is to force the electrons and holes to move towards the opposite side of the material rather than simply recombine in it: thus, there will be a potential difference and thus tension between the two sides of the material,as in a stack "The first ground application of a commercial installation of photovoltaic cell was developed in Japan in 1966. In the picture: 1 - PV Modules 2 - Regulation and Control 3 - Battery 4 - Inverter to power.... 220V