07/06/2025 12:39 p.m.
http://cablematic.iskra.cat/en/products/parallel-cardbus-card-1-port-TP052/
http://cablematic.iskra.cat/en/products/parallel-cardbus-card-1-port-TP052/
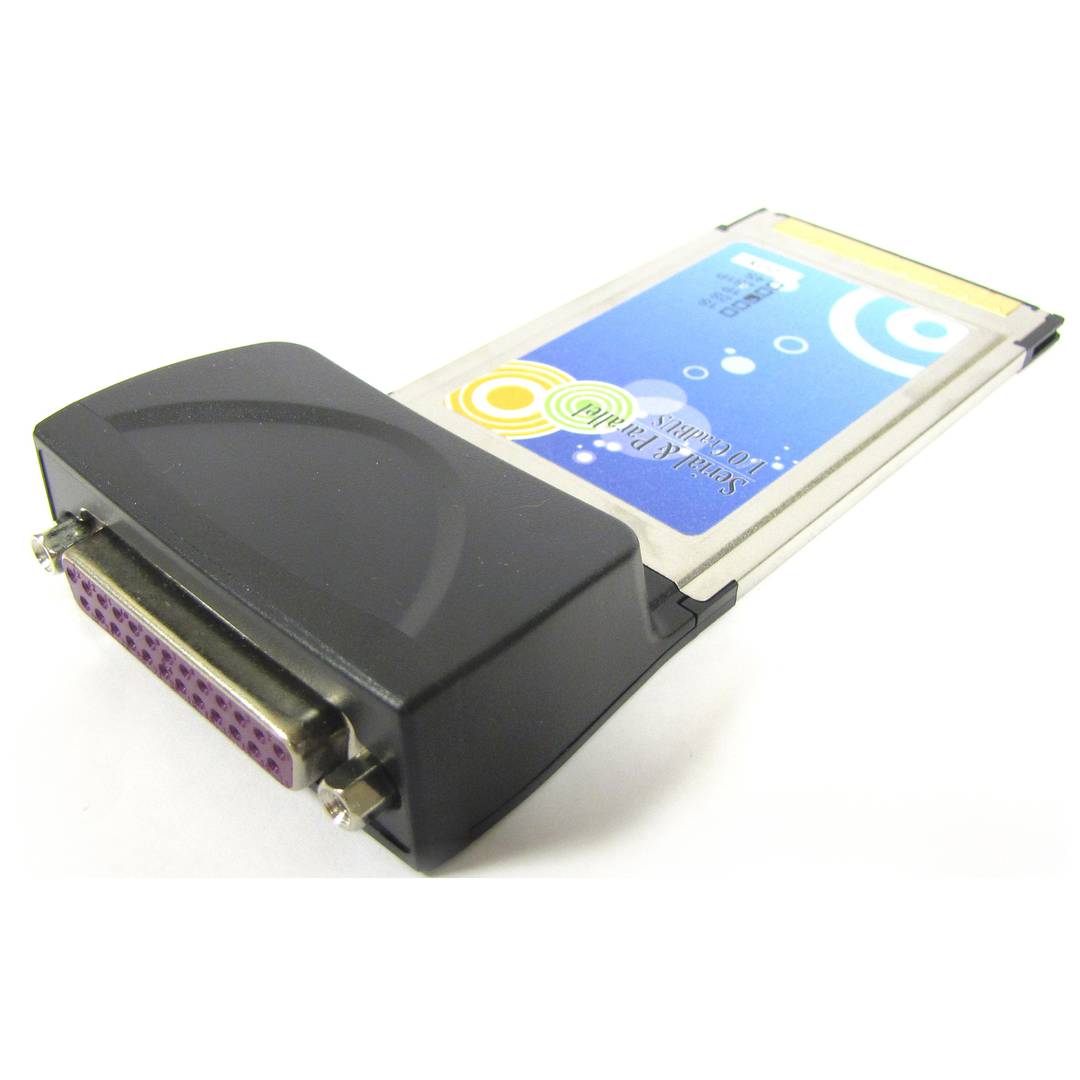
Parallel CardBus Card (1-Port)
REF: TP052
OUTLET
Specifications
- Card compatible with the CARDBUS 32-bit type II slot standard and with an IEEE1284 SPP/EPP/ECP parallel port.
- Data transmission speed of up to 2.7 MB/s.
- Port of IRQ and I/O totally PnP.
- 32 byte FIFO Buffer.
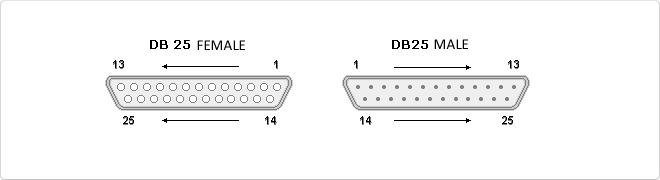
- The card has a DB25-Female connector.
PVP
€9.37
€6.65
Price including VAT:
€8.18
PVD
€8.22
€5.84
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
warranty
returns
OUTLET
Specifications
- Card compatible with the CARDBUS 32-bit type II slot standard and with an IEEE1284 SPP/EPP/ECP parallel port.
- Data transmission speed of up to 2.7 MB/s.
- Port of IRQ and I/O totally PnP.
- 32 byte FIFO Buffer.
- The card has a DB25-Female connector.
More info
Card compatible with the CARDBUS 32-bit type II slot standard and with an IEEE1284 SPP/EPP/ECP parallel port. Data transmission speed of up to 2.7 MB/s. Port of IRQ and I/O totally PnP. 32 byte FIFO Buffer. The card has a DB25-Female connector. Compatible with Windows 98/ME/2000/XP and Linux environments.
- Gross Weight: 210 g
- Number of packages: 1
Technical terms
- Parallel
- IEEE 1284
- EPP
- ECP
- SPP
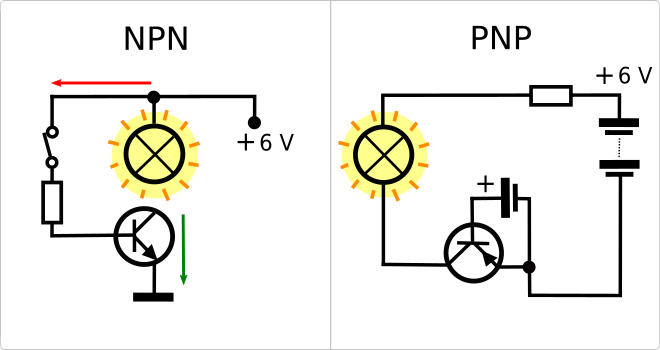
- Differences between PNP and NPN
Parallel
Parallel cable is the cable for computers defined by the IEEE 1284 standard for connecting peripherals via the parallel port. It is often used for connecting printers compatible PC computers. It is considered an outdated connection and has been replaced by USB. - IEEE 1284 Type A: 25-pin DB-25 IEEE 1284 - IEEE 1284 Type B: 36 Drivers, Champ type Centerline Connector 0.085 insurance (Centronics). - IEEE 1284 Type C: 36 conductors, connector type mini Champ de Centerline 0.050 with secure clip (mini Centronics).