07/22/2025 2:38 p.m.
http://cablematic.iskra.cat/en/products/wireless-beltpack-microphone-uhf-82500-to-84975-mhz-group-g2-XW015/
http://cablematic.iskra.cat/en/products/wireless-beltpack-microphone-uhf-82500-to-84975-mhz-group-g2-XW015/
PVP
€26.76
€6.96
Price including VAT:
€8.56
PVD
€23.53
€6.12
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
warranty
returns
OUTLET
Specifications
- Operates in UHF from the range 825.00 to 849.75 MHz.
- RF power output: 15 mW.
- Dynamic soundmonkey.
- Response frequency: 50 Hz to 15 kHz.
- Antenna incorporated inside the microphone.
Keywords
Did not find what you were looking for? These topic could help you
More info
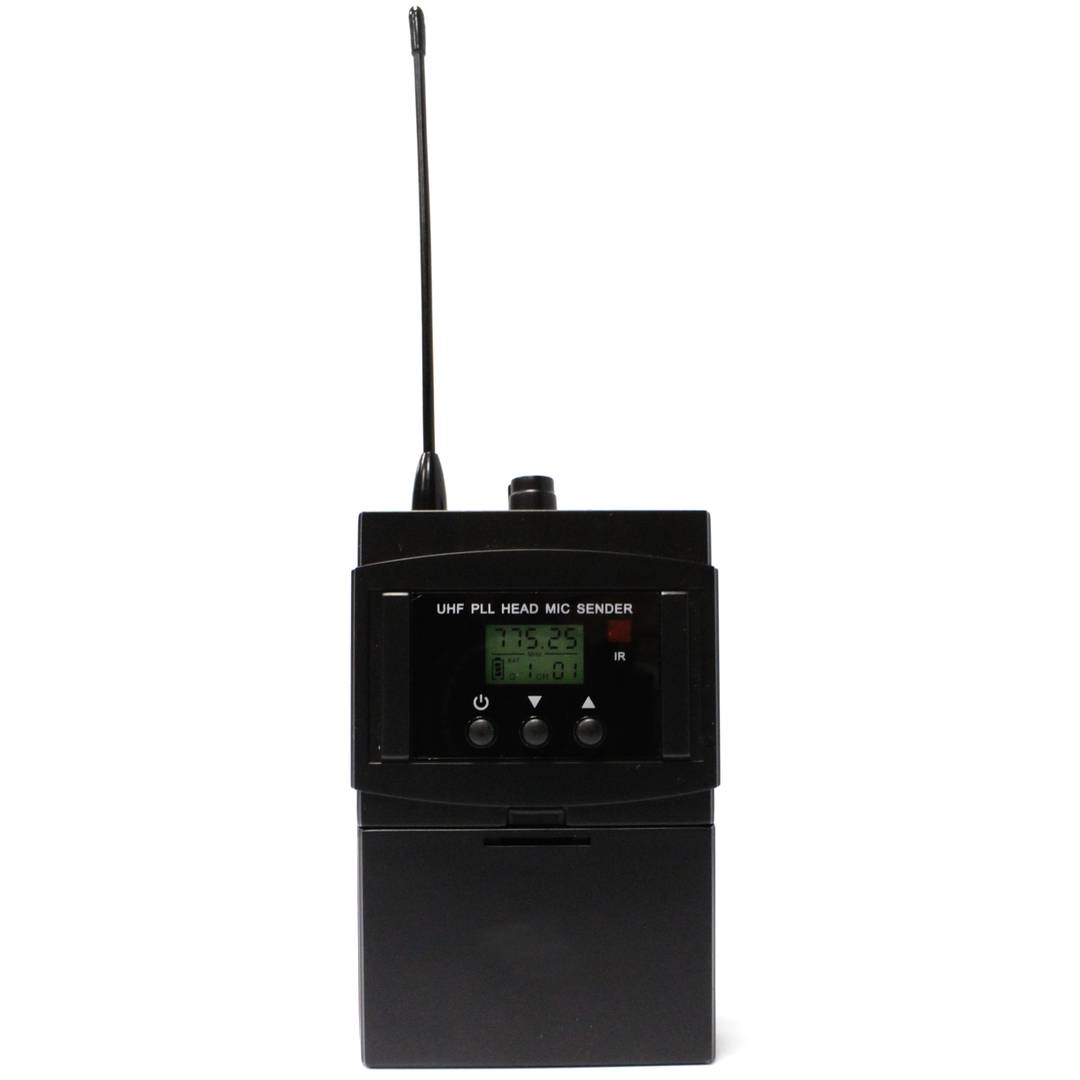
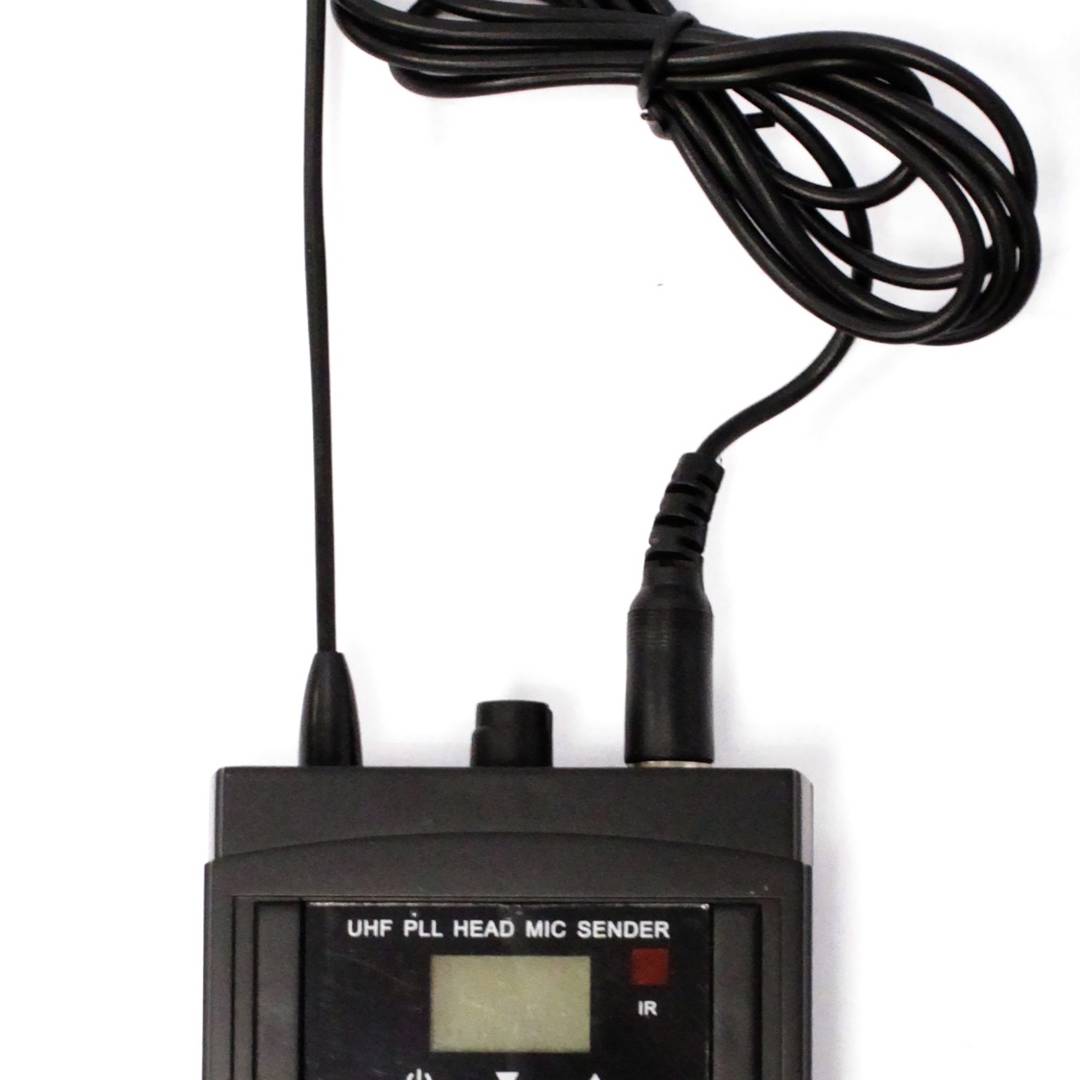
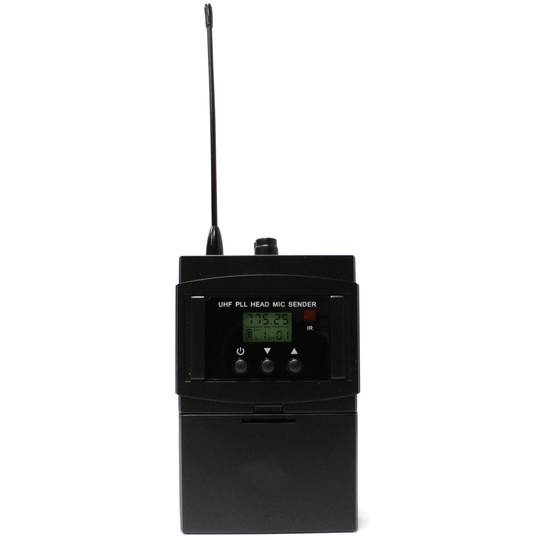
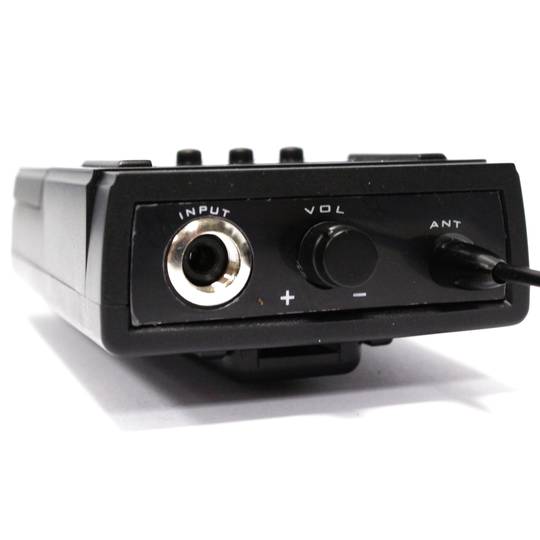
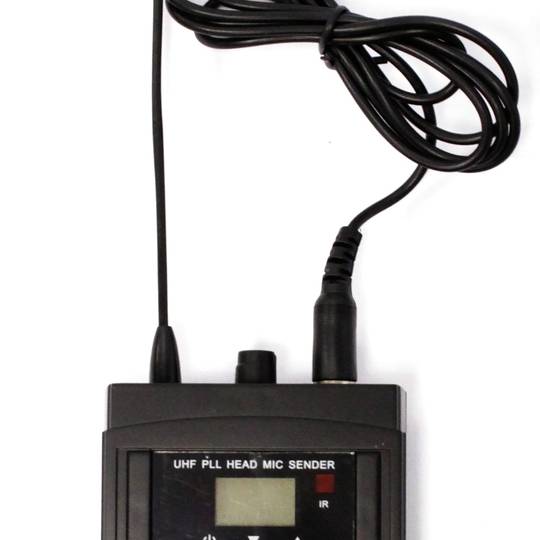
Headset-type microphones for the professional system of wireless microphones with transmission in the UHF band. Microphone designed to be used in conjunction with a UHF receiver of wireless microphones. Model that consists of two parts: an earphone and a pouch.
Specifications microphone
Specifications microphone
- Operates in UHF from the range 825.00 to 849.75 MHz.
- RF power output: 15 mW.
- Dynamic soundmonkey.
- Response frequency: 50 Hz to 15 kHz.
- Antenna incorporated inside the microphone.
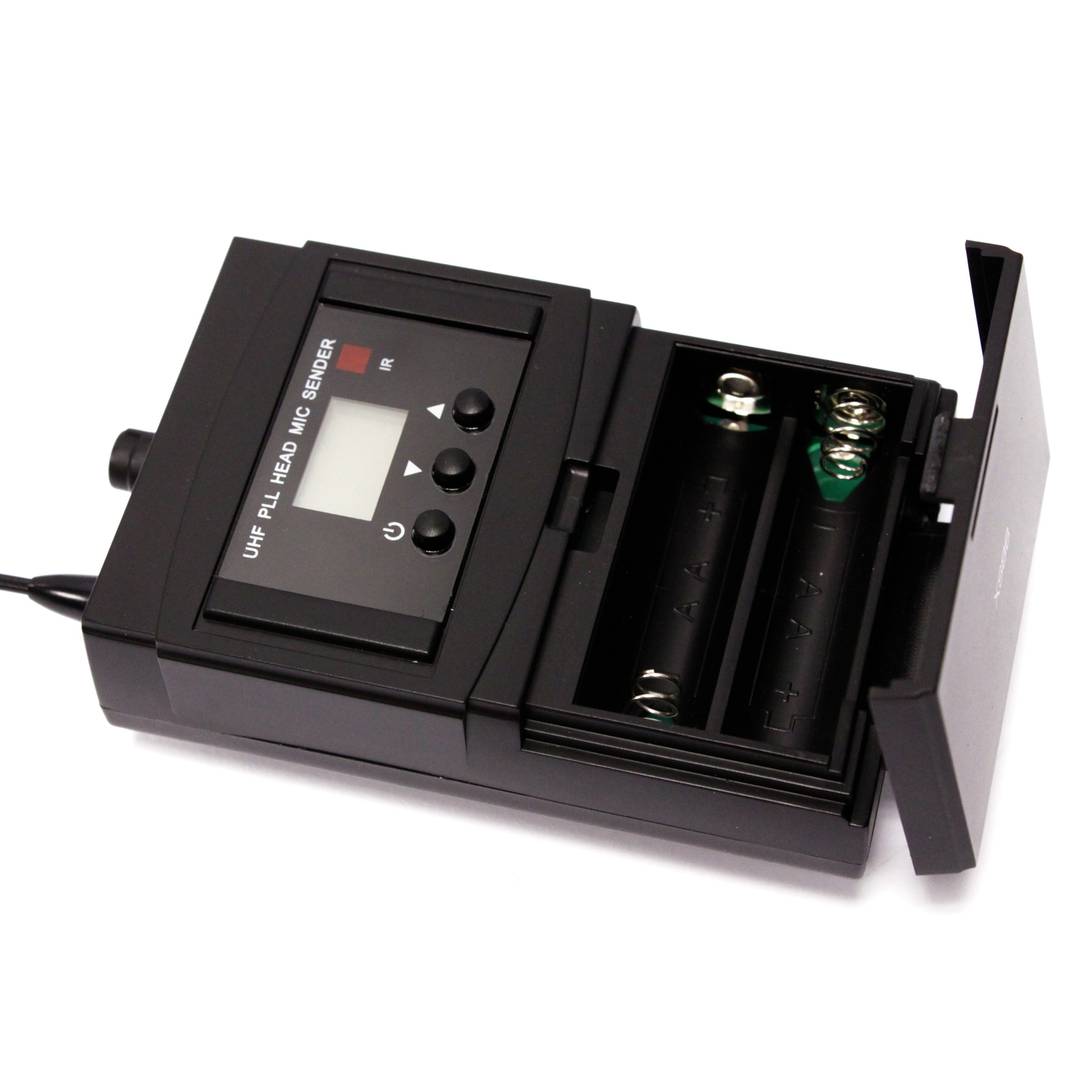
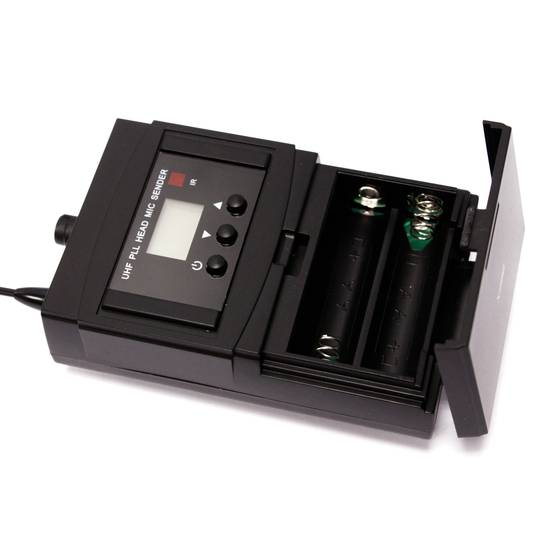
- It works with 2 AA batteries of 1.5 VDC (not included).
- Size of the pouch: 95 x 60 x 32 mm.
- Weight: 320 g.
- It has ON/OFF, UP and DOWN buttons.
- LCD viewer.
- Consumption: 35 mA.
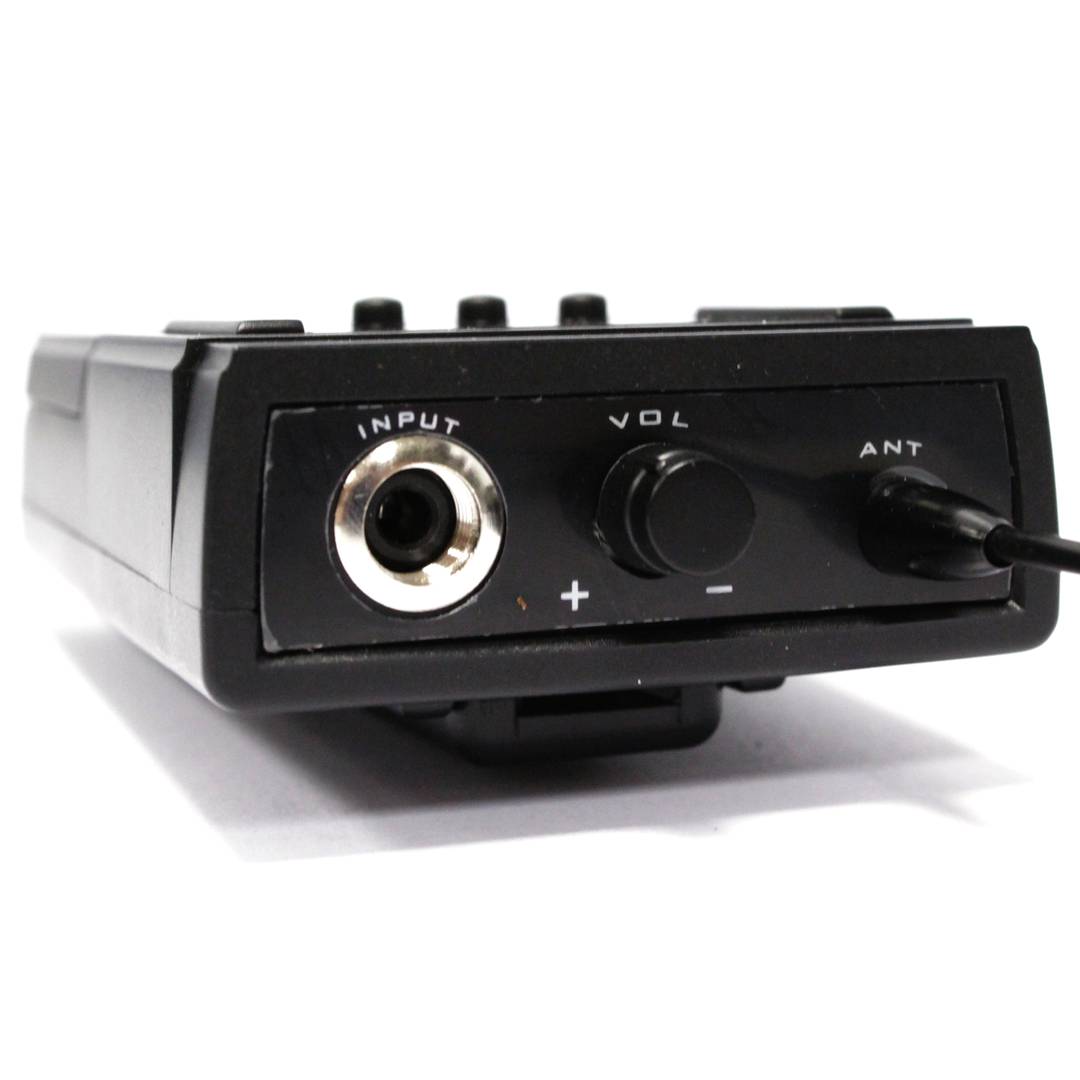
- No microphone is included. Compatible with the model of microphone for hip flask, reference #XW18./ li>
- Gross Weight: 130 g
- Number of packages: 1
Technical terms
- Hz
- UHF
- UHF band
- VDC
Hz
One hertz is one cycle per second, meaning repeating cycle as an event. For example, hertz is applied physics measuring the number of times for a second wave (either acoustic or electromagnetic) is repeated or can be applied, among other uses, to ocean waves that reach the Beach vibrations per second or a solid. The quantity that measures the frequency hertz is called,in this regard, the inverse of the period. One hertz is an oscillation frequency of suffering a particle over a period of one second.